




Visit the old town and discover unusual places. With your smartphone, walk the streets of Toulouse and solve the puzzles hidden among the historic monuments
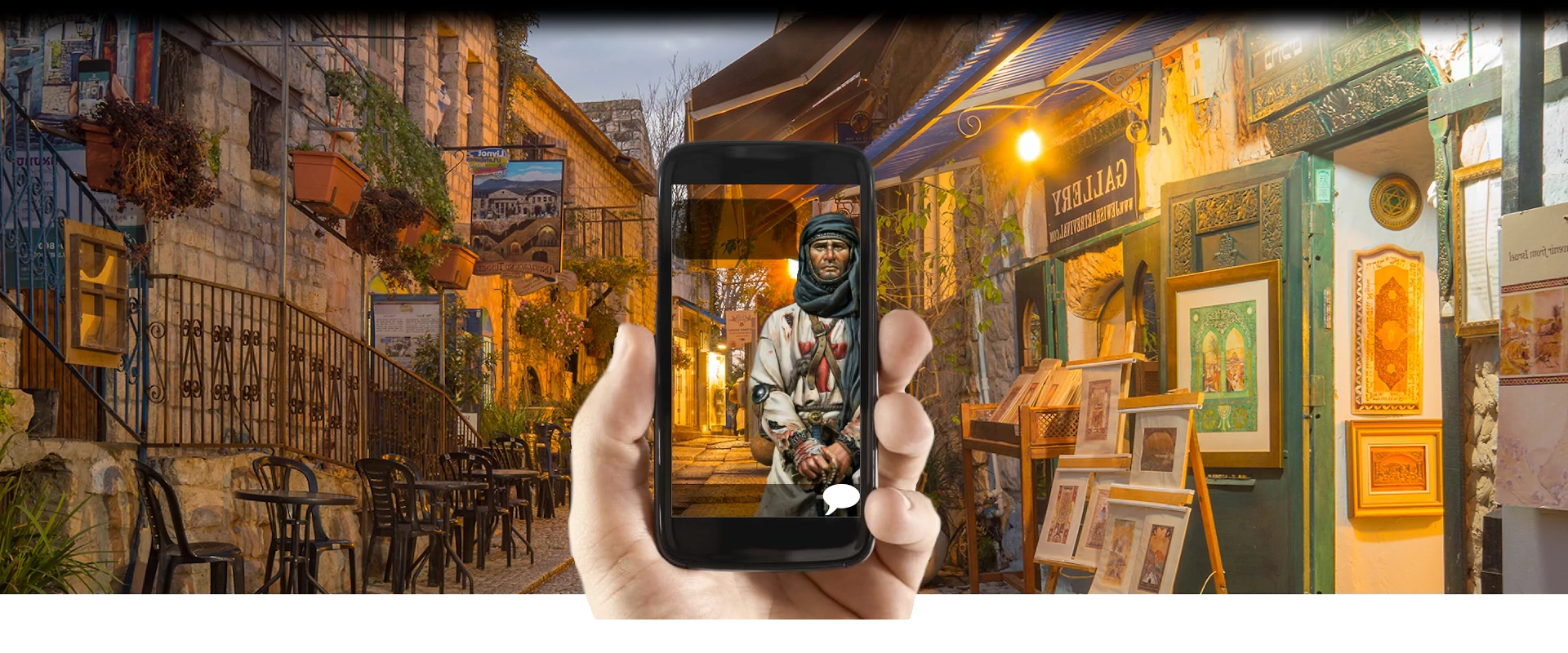
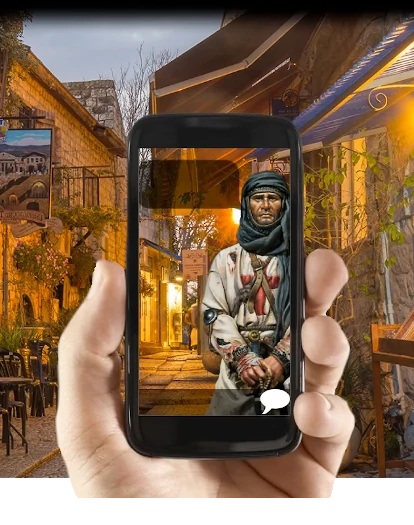







Your friend Louise, carchitect and responsible for the restoration of the Hotel Assézat, has discovered in the basement under the castle an old Cryptex dating from the time of the crusades. Esoteric inscriptions are engraved on the mysterious object.
She needs your expertise in symbol interpretation to discover the secret it contains.
During your adventure, you will meet celebrities from the city and discover its historic monuments, where puzzles have been hidden by an occult brotherhood: «The Knights of the Golden Cross»


This adventure uses the same mechanisms than the «escape game». The rules aren't explicit. The player must guess what he has to do next by considering the elements available in-app and around him.
No other knowledge except these elements are needed to resolve the enigmas. Be vigilant, you will always need to use elements from the urban decor to solve each puzzle.


The adventure is based on characters, documents and historical facts related to the city of Toulouse.
You will travel through the old town and discover iconic places such as the Pont Neuf spanning the Garonne, la Daurade , the Esquirol district , the Place du Capitole or the particular Renaissance hotels. You will have the opportunity to visit the Jacobins Convent , the Augustins Museum or the Basilica of Saint Sernin.
You will discover the history of the city by meeting characters such as the architect Nicolas Bachelier , the Visigothic king Theodoric 1st , the bishop Saint Sernin , the very rich Jean de Bernuy, the count Raymond of Toulouse or even Tholous the king of the Volques.


Once everyone on your team has downloaded the app, go to the metro station Esquirol (line A).
See the MapWhen you have arrived at the departure point, open the application and click on the button:
«Let's start the Adventure»
The adventure can be done entirely offline. You will not need an internet connection during the game.



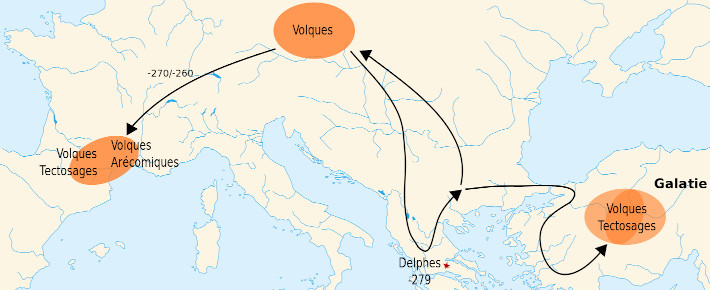
Although the banks of the Garonne have been occupied since Palaeolithic times, the first known inhabitants are part of the Celtic tribe of Volques Tectosages. They are originally nomadic and inhabit the region of Bohemia. In the 3rd century BC, they took part in the Great Expedition, a military campaign where Celtic armies invaded Greece and looted the sanctuary of Delphe. They amass a treasure made of pure gold. They then settled down in the 3rd century BC on the banks of the Garonne where they built Oppidum.
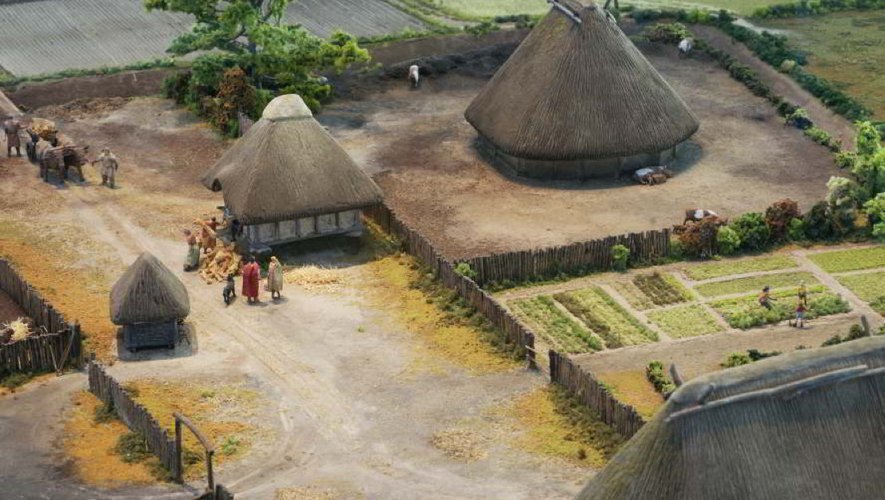

When the Romans settled in the region, they allied themselves with the Volques to keep the peace. When the Teutons invaded the region in 106 BC. J.-C, the city was conquered by betrayal and plundered by the general Roman Quintus Servilius Caepio. According to legend, 70 tons of gold were stolen. On the way back to Rome, the army was attacked by bandits and no one knows what happened to this treasure.
The city prospered thanks to the wine trade and had a population of 15,000 inhabitants in the 2nd century. A 12-meter-high wall then surrounded the city walls. The city became famous in the Roman Empire because of its school of rhetoric.

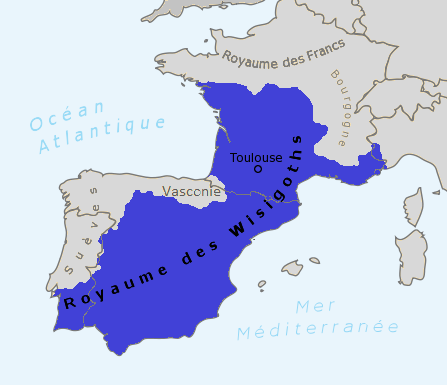
The city was conquered by Visigoth in 460 and Toulouse became their capital. At this time, Christianity took off with the construction of the Saint-Sernin basilica, the Saint-Étienne cathedral, the Daurade church and the Saint-Pierre-des-Cuisines church. Under the influence of its rulers of Germanic origin, Arianism made a breakthrough. In this Christian doctrine, Jesus Christ is only the son of God but not God himself.
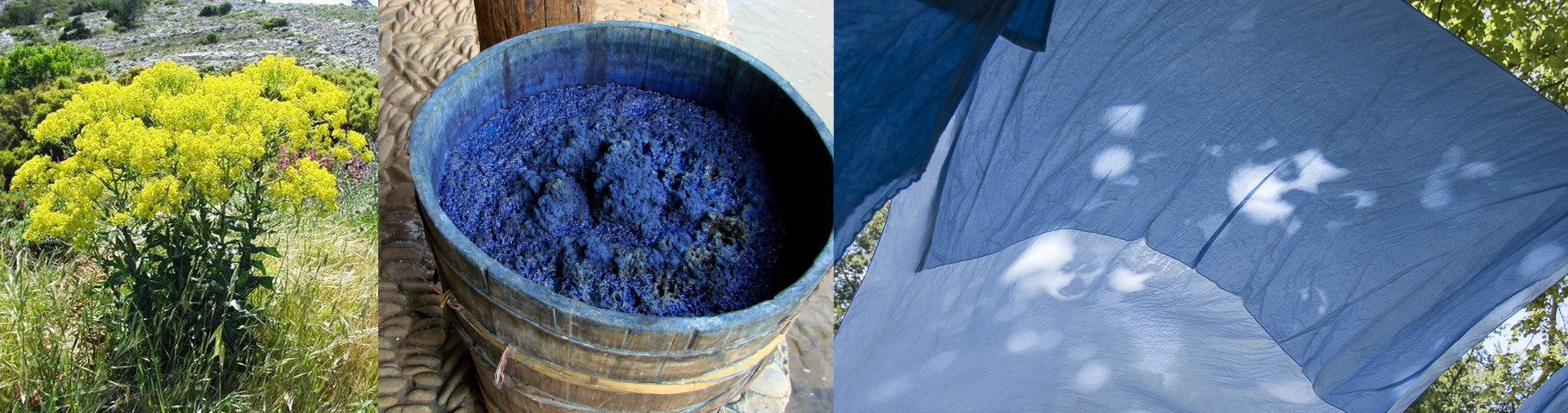
The 15th century was marked by the golden age of Toulouse with the trade of the pastel, a plant that gave the color blue to luxury linens. The city's merchants are getting richer. Many architectural achievements of the city were carried out at this time. The following two centuries will be darker with the massacre of Protestants and several epidemics of plague. The French Revolution resulted in the abolition of the administration of the city by the capitouls which was replaced by a town hall.

Au cours du XXème siècle, Toulouse accueille plusieurs vagues d’immigration de populations italiennes et espagnoles fuyant le régime fasciste de leur pays d’origine. Aujourd’hui, la ville connaît une forte croissance avec 15000 nouveaux habitants chaque année. Son économie est florissante grâce notamment au secteur de l'aéronautique avec Airbus et l’industrie spatiale.
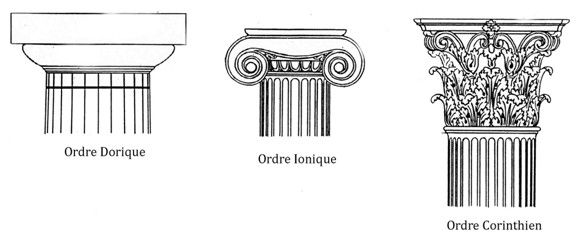
This building was built during the heyday of the pastel trade during the Renaissance in the 16th century. It was built by the architect Nicolas Bachelier for Pierre d'Assézat, a wealthy pastel merchant. This building is one of the first building of the French classical style. This style was invented to magnify Louis XIV. This architecture is inspired by the aesthetic canons of antiquity with a search for symmetry, simple lines where the details respond in harmony to the whole.

The courtyard is made of brick but the decor is in stone creating an aesthetic effect. Two of the sides of the courtyard have a three-level elevation superimposing the three classical orders (Ionic order, Doric order, Corinthian order) typical of the Renaissance.
Son of a Toulouse architect, he went to Italy, Rome and Florence at a very young age to improve his skills. He notably follows the teaching of Michelangelo. On his return, a councilor of the city's parliament entrusted him with the construction of a mansion. It adds elements inspired by the Italian Renaissance. His work makes an impression. Subsequently, the notables of the city called upon his services for their construction. He was celebrated after his death as the city's greatest architect.

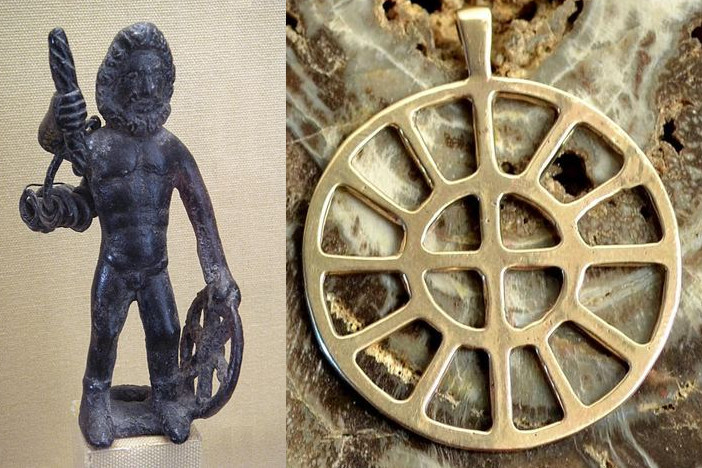
Taranis is one of the major gods of the Celtic pantheon. He is often represented with a sun wheel. It symbolizes the passage of the seasons. He is often accompanied by a horse, a snake or an eagle in order to transport the souls of the deceased to the other world. He was then associated with the god Jupiter during the assimilation of the Celts by the Romans. His worshipers used the sun wheel as a talisman.

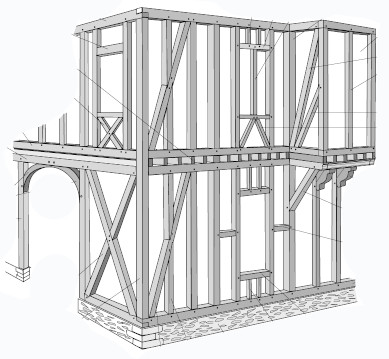
This house was built in the 16th century. There are more than two hundred half-timbered houses in Toulouse. This type of construction appeared in Roman antiquity and then spread to France during the Middle Ages. The framework is wooden and the walls are filled with cob, plaster or bricks. The cross beams have a meaning: they represent the cross of Saint Andrew, a Christian martyr crucified on an X-shaped cross. It protects the house against fires. The cross has a second meaning, the X is also a multiplied sign which symbolizes fertility.
In the 5th century, the Visigoths were sent by Rome to Gaul to fight other barbarian invaders. They receive Aquitaine as a reward for their service. On the death of their general, Theodoric was elected king by the nobles and he established his capital in Toulouse. He led his army in hispania and annexed several kingdoms. He died during his participation in the Battle of the Catalan Fields, a great battle marking the end of antiquity: A coalition between the Romans and several barbarian kingdoms (Visigoth, Burgund, Franks) that stopped the invasion in the north of France by the armies of Attila the Hun.

Euric is the son of Théodoric 1st. He inherits the crown of the Visigoths after the assassination of his two older brothers. In order to strengthen the cohesion of his kingdom made up of different peoples (Celts, Romans, Germain), Euric write an important code of laws which includes 330 chapters. It will be widely disseminated in Western Europe and lays the foundations for medieval legislation. Relations between vassals and lords are codified. In order to avoid revenge between families, murders and mutilations are reparable against standardized financial retribution.

The Place de la Daurade takes its name from the Occitan "daurado" which means golden. 1500 ago a church in honor of the virgin mary was built here. A golden mosaic adorned its interior. Since the Middle Ages this place was used as a commercial port. It was also the place where the sand merchants could be found: the sand was raked at the bottom of the Garonne and then mixed with lime to make cement. The glacier below was the old mortuary. It was used to store the corpses of drowned people recovered from the Garonne.
Also known as Saint Sernin, Saturnin is the first bishop of Toulouse. In the 3rd century, he was sent by the Pope to evangelize the Gaul. As he passed in front of a Roman temple, pagan priests asked him to honor the emperor by sacrificing a bull to him. He refused and was tied to the bull of the sacrifice. The bull rushed down the temple steps, dragging the bishop behind him. His head exploded on the steps. The street that the bull then took was named in reference to this event, rue du Taur.

The Hôtel de Bernuy was built in the 16th century and marks Toulouse's entry into the Renaissance. The portal is in the Flamboyant Gothic style. This style is characterized by the use of mouchette and soufflet that recalls the shape of the flame.

One can see on the portal four sculpted busts: Jean de Bernuy, his wife and his two children. SI DEUS PRO NOBIS is engraved in the middle of the angelos. This is the motto of the Bernuy family which means "If God is with us, who will be against us? ".
Bernuy's family, of Spanish origin, settled in Toulouse in the 15th century. While the pastel market was flourishing, Jean de Bernuy bought large quantities to control the market. He reinvests all his earnings in land, buying castles and estates. He thus becomes extremely rich. In 1525, François 1st was taken prisoner by Charles Quint. The Spanish monarch demands the Duchy of Burgundy in exchange for the release of the French king. Jean de Bernuy intervenes by paying a ransom of two million ecus.

The word “blue” appears in the Middle Ages. Previously, this color was referred as a shade of green, white or black. This color being extremely rare in nature, no word designates it in most primitive languages. This color is also difficult to obtain as a pigment, so it is used in luxury drapery. In Europe, dyers use the pigment extracted from a plant called Guède. This plant grows mainly in the south of Toulouse. Its cultivation ensured the wealth of local merchants until the discovery of indigo in the 16th century in South America, a plant that was easier to grow and richer in blue pigment.

The buildings bordering the square date from the early 19th century and are neoclassical in style. This style appears as a result of the discovery of important archaeological sites such as Pompeii. It therefore differs from the classic style by being closer to ancient achievements. It contrasts with the previous styles, Baroque and Gothic, by the scant use of ornamentation and sculpted reliefs.
The first construction of the Capitol was ordered in the 12th century when the Capitoulat system began. In this system the city is directed by an assembly of magistrates, the Capitouls. Each one is elected by a different district. They then automatically become noble and enjoy a certain autonomy from royal power. Their power is not limited only to the city but extends over the entire surrounding region. Their attributions are very broad: municipal services, judicial power or even military command.
In the 9th century, the Duke of Aquitaine went to war against the King of France. Raymond, Count of Rouergue, supports the king and receives the County of Toulouse for this betrayal. He becomes Raymond 1st and found the Raimondine dynasty by becoming the first hereditary count of Toulouse. Raymond IV distinguished himself during the First Crusade by commanding one of the 4 armies.
The Occitan cross appears in the 9th century on the emblem of Raymond, Count of Toulouse, but its origin remains mysterious. Among the hypotheses, this cross could come from the Celtic sun wheel, attribute of the divinity Taranis. The symbol would have been used by the Celtic tribe of Volques in the 3rd century BC. The twelve golden disks indicate the twelve months of the year, symbolized by the signs of the zodiac affixed to the center of the Capitol Square.

The volques tectosages are a nomadic Celtic people originally from Germany. In the 3rd century BC, they took part in the "great expedition": a coalition group of Celtic tribes invading Thrace, Macedonia and Greece. They take advantage of the disintegration of the empire of Alexander the Great. The Volques looted many temples, including the famous temple of Apollo in Delphe, and took their booty to the south of France. Legend tells that the gold stolen during these lootings is cursed by the gods. The fraction of the tribe that founds the current city is called the Tolosate.
The building along rue Alsace Lorraine was built in the 19th century. You can see engraved under the arches the list of artists exhibiting in the museum. The rest of the museum is housed in the former Augustinian convent built in the 14th century.
In the 3rd century BC, during the great expedition, a Celtic coalition invading Greece, the Volques plundered the temple of Delphe and seized 70 tonnes of gold. They then settled on the banks of the Garonne and founded the city of Toulouse. A century later, the Roman general Quintus Servilius Caepio loots the city and recovers the spoils of the Volques. As he was bringing the cursed gold back to Rome, brigands attacked the convoy. The general was accused by the Roman Senate of having ordered this attack to appropriate the treasure. Following this accusation, he was sentenced to exile.